How did Nigeria fare in telecoms 2019? These are the 10 areas where the industry regulator and stakeholders record noteworthy achievements to keep the sector attractive and competitive heading into year 2020.
2019: 10 Areas Nigeria Recorded Huge Success to Boost value-chains in Telecoms Industry
Synopsis:

Note that government through the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC), in 2019, carried out a number of regulatory activities towards ensuring increased access to telecoms services, ensuring increased consumer education and protection, boosting security of life and property, sanitising the industry while also supporting other initiatives that are aimed at boosting innovation for the country’s overall economic growth.
Improving Quality of Service on Networks
As part of its move to improve Quality of Service by promoting the availability of reliable, interoperable, rapidly restorable critical ICT infrastructure that are supportive of all required services, the Commission, in the course of the year, reviewed 2G Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and development and definition of 3G/4G QoS KPIs for collocation service providers as well as Internet Service providers (ISP).
During the year, the NCC also developed the New National Numbering Plan. Based on recent developments in the global telecommunications industry such as machine to machine (M2M) communications, the Internet of Things (IoT), Over-the-Top (OTT) and others, as earlier stated, and other services made possible by fourth-generation networks and the futuristic 5G/6G technologies, the NCC has considered it imperative for the numbering plan in the country to be reviewed. The development of the new NNP, therefore, will help to provide numbers that will satisfy the needs of the projected 500 million Nigerians to be connected and about 1 billion globally-interconnected machines and devices by 2050; promote efficiency in the allocation of this scarce national resource; promote competition among service providers; eliminate the risk of running short of all categories of numbers; facilitate the introduction and development of new and innovative services and above all, encourage growth of the telecommunications sector and the attendant job creation and contribution to National Gross Domestic Product (GDP), among others.
The Commission ensured type Approval of End User Devices to certify that Quality of Service/ and Quality of Experience (QoE) experienced by the user is not negatively impacted. This is to prevent counterfeit devices in the Nigerian Market through Equipment Authorization. The Commission has also continued to monitoring point interconnection performance among operators and ensure resolution of interconnect disrupted among operators to prevent serious impact on quality of service received by the consumers. The Commission also ensured Quality of Service Performance Monitoring through continuous monitoring of service delivery by the operators to ensure compliance.
The Commission also intensified collaboration with necessary stakeholders and government agencies at Federal and state levels towards resolving critical industry challenges affecting faster deployment of telecoms infrastructure in the country. These include right of way issue, multiple taxation and regulations, vandalism, indiscriminate closure of base stations, fibre cuts, among other.
Boost in consumer education, empowerment & protection

In line with the number 6 of the 8-Point agenda of the Commission, which addresses protection and empowerment of telecom consumers and in sync with its PIE Mandate (Protection, Information and Education of the consumer), the NCC has carried out a number of consumer-centric activities during the year.
From January to October, 2019 the Commission received a total of 19,841 complaints from consumers out of which 17,851 were successfully resolved to the satisfaction of telecom consumers. The number of complaints resolved represents approximately 90% of the total complaints received through the various channels of lodging complaints. It also ensured continuous monitoring of the Customer care centre of the service providers in the 36 states of the Federation to ensure efficiency and effectiveness of centres to the benefits of telecom consumers. It also leveraged its various Consumer Education Outreach Programmes to educate a total of 35,124 telecom consumers on various issues such as how to avoid data depletion, importance of SIM registration, what to do during SIM replacement, need to protect telecom infrastructure, call masking, EMF, how to mitigate effects of cybercrimes etc. This was achieved through the Consumer Townhall Meetings, Consumer Outreach Programmes, Telecom Consumer Parliament and Trade Fairs & Exhibitions.
With regards to unsolicited text messages, based on frequent complaints received from consumers, the Commission developed the DND 2442 Short Code to stop unsolicited text messages and calls. As at October 2019, a total of 22,356, 919 consumers have activated DND Service. Of this figure, 21,913,565
(98%) are full DND subscriptions while only 443,354 (1.9%) are partial DND. This has so far led to a significant drop on complaint on unsolicited text messages and calls in recent time. Also, the NCC Toll-free Number 622, created as an additional channel for aggrieved consumers to lodge their complaints has continued be more popular among the consumers. From January to October, 2019, a total of 18, 717 complaints were lodged through the NCC contact centre by the customers to the Commission via the initiative.
Based on their satisfaction with all these facilities provided for the consumers, the NCC received commendations/appreciations from 19,345 satisfied consumers through calls to NCC Contact Centre and e-mails received via Consumer Web Portal for its various interventions in satisfactorily resolving their complaints.
Also this year, the Commission unveiled a REVSIED Consumer Complaints & Service Level Agreement (CC/SLA) to improve consumer complaint management and resolution in a more promptly matter by the service providers. Similar efforts championed by Danbatta-led NCC in the course of the year to address consumer issues, is the inauguration of a multi-sectoral committee to combat the issue of financial losses through telecoms or digital platforms.
The 26-man committee draws membership from the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), the NCC, Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Commission (FCCPC), Nigerian Inter-Bank Settlement System (NIBSS), National Identity Management Commission (NIMC) and the Association of Licensed Telecom Operators of Nigeria (ALTON). Other organisations with representation on the Committee include the banks, security agencies such as the Office of the National Security Adviser (ONSA), the Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC), Independent Corrupt Practices other Related Offences Commission (ICPC), Nigeria Police Force (NPF), Nigeria Financial Intelligence Unit (NFIU) and the Federal Ministry of Justice.
Also in the year under review, NCC intensified regulatory efforts towards protecting the interests of telecoms consumers from the scourge of financial frauds. It demonstrated this at the 2019 fourth quarter Open Forum of the NCC’s Industry Consumer Advisory Forum (ICAF) in Abuja on Tuesday December 12, 2019. The forum was attended by ICAF institutional and other stakeholders from telecom and financial sectors, law enforcement agencies as well as consumer advocacy groups, all of who convened at the instance of NCC to deliberate on financial frauds using the telecoms platform. The deliberations focused on what consumers need to know in order to be protected. Thus, the forum provided opportunities for stakeholders to examine and address criminal acts perpetrated using telecommunications channels. Participants called on banks and telcos to step up measures to create robust awareness in order to ensure that telecoms platforms are used to carry out financial transactions safely.
Speaking at the ICAF forum, Adeleke Adewolu, Executive Commissioner, Stakeholder Management (ECSM), NCC, said there has been growing concern over the rising trend of electronic frauds across key sectors of the Nigerian economy with Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) rating e-fraud as the biggest risk on the financial sector where the use of e-channels to conduct financial transactions has become the order of the day. He said telecoms sector is not immune to the scourge of electronic-related frauds, as attackers now target telecoms networks with the intent to disrupt service delivery and infiltrate their data banks. “Illegal subscriber identification module (SIM) swaps and Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD) e-payment frauds, are currently some of the most serious cyber threat in the telecoms industry. Fraudsters conduct illegal SIM swap of targeted individuals and then, conduct USSD-based transactions which cost the victims huge losses,” Adewolu said.
Also, through the Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement Department of the Commission, also protects the consumers and ensures consumer quality of experience by attending promptly to complaints escalated to us and sanctioning the affected Operator(s) on any breach against the consumer. Adverts and promos are monitored to ensure consumer quality experience, promote market growth, ensure fair competition and prevent consumer exploitation. The Department also sanctioned mobile network operators (MNOs) on behalf of consumers for forceful subscriptions and unapproved/deceptive adverts.
In line with relevant sections of the Nigerian Communications Act (NCA) 2003, the NCC carried out Enforcement action against companies operating without Licence and unapproved transfer of ownership or Licences. This has aided the Commission in achieving its agenda on Regulatory excellence and operational efficiency. In the course of the year, it conducted routine monitoring of licensees/service providers compliance with the terms of their license condition and obligations. Other activities of the Commission in this regards include: Compliance Monitoring Exercises on Operators’ License conditions; Coordination of Surveillance & Intelligence Gathering exercises; Technical Audits on the Mobile Number Portability (MNP) Scheme; Compliance Spot checks relating to new and existing Directions, Guidelines & Regulations of the Commission; Regulatory Intervention meetings with Stakeholders on Cases of Multiple Taxation and removal of barrier for the deployment of telecoms infrastructure; Enforcement raids on pre-registered SIM Cards and Illegal operators in the Market; and Site Investigations into complaints regarding the installation of Masts & Towers in the telecoms industry.

Advancing broadband penetration
As part of its efforts in advancing broadband penetration, which topped its 8-Poing Agenda, the Commission has succeeded in issuing six InfraCos to drive the deployment of broadband infrastructure across the nation’s six geo-political zones and Lagos. The licensees are include Raeana Nigeria Limited for the South-South Zone; O’dua Infraco Resources Limited for South-West Zone; Fleek Networks Limited for North-West Zone; Brinks Integrated Solutions for North-East Zone; MainOne Limited for Lagos Zone and Zinox Technologies Limited for the South-East Zone. The remaining licence for North Central Zone is being processed, according to the Commission. This year, increased regulatory is already being made the Commission to seek Federal Government’s approval of the counterpart funding to be disbursed to the InfraCo to facilitate their deployment. The finding will, however, be given to them upon attainment of deployment milestones, according to the Executive Vice Chairman of the NCC, Prof., Umar Danbatta. The InfraCos which is based on the Open Access Model (OAM) initiative of the Commission will ensure there is, at least, one fibre Access Point for digital services across the 774 local government councils in the country. Increased commitment was given to this by the Commission.
In this regard also and with respect to spectrum that will support broadband deployment, the Commission, this year, approved the 5 G trial on 3.5 GHz and 26 GHz to MTN; developed guidelines on the use of Television White Space (TVWS) to facilitate broadband penetration to underserved and unserved areas; opened up of 60 GHz band for unlicensed applications and broadband services; approved the use of 18 and 23 GHz Microwave Frequency bands for point to multi point deployments.
Also, the Commission has licensed some portions of 5.4 GHz bands; replanted the 800 MHz band for LTE; assigned 2×10 MHz Spectrum to Glomobile for trial in the 700 MHz; approval of Globacom trial on the 2×10 MHz assigned to it. It expired in February, 2019 and the company has been offered right of first refusal on the slot. The NCC has also reegularized 2×10 MHz Spectrum in the 700 MHz band previously assigned to MTN by NBC for the frequency to be used for the purpose of providing LTE services.
Another regulatory efforts carried out this year in this regard was the creation of Space Services Unit within the department to enable us regulate satellite and space services in facilitating broadband penetration; regularisation of the activities of all satellite operators including Space station operators as well as Earth Station operators; as well as issuance of Landing permits to Space Stations beaming signals over Nigerian territory.
Promoting ICT Innovations

In keeping with its ongoing tradition of driving technology innovations through funding relevant researches in tertiary institutions, the Commission, in May 2019, announced N40 million endowment fund for Bayero University, Kano and the Federal University of Technology, Owerri. The fund will be utilized by the institutions for innovation, research and development in the digital space with an ongoing commitment to expand the list of benefiting institutions. Also, in June 2019, the Commission again demonstrated its determination to facilitate research and innovation in the telecom industry in Nigeria by presenting the sum of N65 million to eleven (11) universities in Nigeria for innovation, research and development to deliver research result and prototypes that are implementable, commercially-viable and capable of engendering innovation in different sectors of the economy.
Also in its continuous efforts to support young techno-preneurs, the NCC has been playing a pivotal role in promoting investment opportunities and innovation within the digital ecosystem for economic growth is in exposing young Small and Medium Enterprisers (SME) owners in the ICT industry to global investment opportunities. This is done annually through sponsoring young Nigerian innovators to such global forum as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Telecoms World principally to provide them with the platform to exhibit relevant, home-grown technology innovations and solutions to the global investment community. This year’s edition of the ITU forum has been scheduled to hold in Budapest, Hungary in September, 2019 and in the same manner, the NCC is sponsoring a number of young technology innovators to the conference for the same purpose. It has also held several stakeholder fora with academia across the country towards ensuring proper linkages among the Government, Industry Plater and academic towards developing tech innovation in the country.
Telcos’ listing in 2019 boosted capital Market Operations

One of the remarkable developments witnessed on the economy this year was listing telecoms companies on the Nigeria Stock Exchange (NSE), credit to the Danbatta-led Commission. The listing was one of the positive results of a ‘no-nonsense’, outstanding and effective regulatory effort of the Commission. The listing of MTN has, thus, served as tonic to other telcos to follow in the same direction such as the listing of Airtel. The Commission essentially facilitated the landmark listing of the country’s largest telecommunications operator on NSE in line with its regulatory activities as enshrined in the Nigerian Communications Act (2003) and other subsidiary regulations to promote investment, create a level-playing field for all licensees, ensure compliance to existing telecoms laws and facilitate delivery of top-notch quality of services (QoS) to the consumers.
Through this smart regulation and intervention by the NCC, leading to the listing of MTN on the NSE, the Commission has opened another chapter in the history of telecommunication industry by empowering Nigerians to control, own and manage one of dominant telecommunications companies in the country by owning shares in MTN Nigeria.
“The MTN listing has helped to translate into action, an important objective of the Commission, which is to promote local investment and ownership in the telecom sector. Also, with MTN shares available in the capital market, it is expected that Nigerians will buy shares and by purchasing the shares of MTN, they will be financially empowered and be socially transformed,” Danbatta said at a forum. According to him, “It is instructive to state here that one of the greatest advantages of the MTN listing, facilitated by the NCC, is the implication it has on opening up the telecommunications industry for greater investment profile it gives Nigerians the opportunities to invest in publicly-quoted companies like MTN, which is the leader in the telecommunications industry in the country and easily one of the continental leaders.”
“In addition to benefits to the consumers, we all know that telecoms is a capital-intensive industry and of late, we found out that the inflow of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into the sector has not been as much as it used to be and there is so much for the telcos to still do in terms of expansion and this expansion requires capital. Industry issue bordering on poor quality of service is being partly traced to lack of sufficient infrastructure covering the entire country.
“One of the benefits of MTN listing and those of other operators to follow, therefore, is that the telco would be able to raise capital for expansion which, in turn, will bring about an improvement in the quality of service and quality of experience for the consumers of telecoms services, which is also a cardinal function of the Commission.”
Undoubtedly, despite the high volatility seen in the Nigerian capital market for the year 2019, the listing of the biggest telecommunication companies, MTN Nigeria and Airtel Africa has helped in making the market capitalisation bullish. Today, capital market regulator and shareholders bodies have commended the effort of the NCC in making the capital market thick through facilitating the listing of MTN, which was fallout of the conditions the telecom regulator gave MTN following the telco’s violation of SIM registration rule in the telecommunication sector.
Already, capital market stakeholders have said MTN Nigeria and Airtel Africa listing on the NSE have boosted investors’ confidence and liquidity, even as the nation’s economy stands to benefit. Based on this feat, capital market stakeholders, who have seen the fillip in the market operations brought about by telecoms listing, are now calling for laws that would compel multinationals, oil and gas companies, telecommunication firms and privatised companies to list on NSE to deepen the market.
Boosting security of lives and property via ECC

The Commission, this year, stepped up measures in his implementation of the Emergency Communications Centre (ECC) project to support President Muhammadu Buhari’s administration’s tripartite agenda, especially improving lives and property in the country. Other two agenda of the President are to improve economy and Curb Corruption. NCC’s drive in enhancing security of life and property through the Emergency Communications Centre (ECC) project became fully activated under the leadership of Prof. Umar Danbatta and it got a boost this year.
The Commission’s efforts in this regards culminated in double recognitions that came the way of the Commission on the one hand and the EVC on the other hand during the 1st Security and Emergency Management Awards held in Abuja on Thursday, Dec 5, 2019, where the Danbatta received Goodwill Ambassador on Security and Emergency Management in Nigeria while the NCC, as an organisation received CSR Award on Security and Emergency Management in Nigeria.
Therefore, the Commission has, through increased efforts this year, fully activated and made operational, ECCs in Seventeen (17) States across the country and the FCT as listed below. FCT, Benue, Kwara, Plateau, Kaduna, Kano, Katsina, Ogun, Ekiti, Ondo, Oyo, Edo, Akwa Ibom, Cross Rivers, Imo, Anambra, Enugu and Adamawa. Subsequently, the commissioning of the National Emergency Toll free number 112 and the Katsina State Emergency Communication Centre, representing the North West Zone, was successfully carried out on the 23rd September, 2019.
Furthermore, necessary preparation and arrangements is being put in place to ensure successful launch/commissioning of Centres, including publicity and enlightenment in the remaining Five (5) geopolitical zones and the FCT. Also, as the ECC impacts positively in ensuring safety, security of lives/properties and socio-economic benefits, the Commission is embarking on collaboration with relevant agency to ensure effective and efficient service delivery, facilitate adoption/usage and publicity.
Leveraging TVWS for rural connectivity

Further to the strategic implementation of its 8-Point Agenda, the Commission, earlier in 2019, partnered with the National Broadcasting Commission (NBC) and other industry stakeholders to discuss the introduction of television white spaces (TVWS) in order to develop a framework for effective utilisation of TV spectrum to take services to the unserved and under-served communities in the country.
TVWS is the unused broadcast spectrum which can be deployed in the telecommunications sector to provide cost-effective broadband services to people in the rural, underserved and unserved areas of the country towards achieving universal access and universal service in line with the country’s digital agenda. The collaboration with the NBC was in line with the fifth pillar of the NCC’s 8-Poing Agenda focusing on facilitating strategic collaboration and partnership with necessary government agencies and stakeholders.
The initiative for the use of TVWS in Nigeria mid-wifed by the Ministry of Communications, following approval for the use of the TVWS technology by the National Frequency Management Council (NFMC) will further help the Commission to deliver on its mandate of ensuring universal access to telecoms services in the rural, unserved and underserved areas. “Ensuring that all Nigerians are connected is our priority at the Commission,” Danbatta stated at the stakeholders’ forum held in Abuja on TVWS. “We are continuously in a quest to achieving rural connectivity goal and this quest has led us, as a Commission, into embarking on several initiatives to actualise this pervasive connectivity objective in Nigeria.”
Promoting next-gen 5G revolution in Nigeria

The Commission in November, this year, provided the regulatory platforms for telecoms operators to begin trail of 5G in the country. By this experiment, the NCC became the first telecoms regulator to begin their technology revolution journey in the whole of West Africa. Already, MTN Nigeria, has conducted trial of 5G in Abuja, Calabar and Lagos under the supervision of the Commission. The mid-wifing of 5G technology trial in Nigeria this year by the Commission is sequel to workshop it organized in the last quarter of 2018, in collaboration with the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA) to discuss the prospects and challenges of Next-Generation Networks (NGN) such as the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data, among others, in the nation’s telecoms industry.
Danbatta during the workshop said the workshop was “to provide an avenue for regulators, operators, investors as well as other stakeholders to examine and constructively exchange ideas on the main demand areas for next generation of services, spectrum licensing reforms and the requirements for 5G and other emerging technologies that are to revolutionise the telecom system and users.” The workshop, thus, formed the precursor to the country’s preparedness of the Commission for the impending deployment of 5G services due to commence globally by 2020.
With the trial of 5G ongoing, preparatory to the actual commercial launch starting from 2020, industry stakeholders have commended the Commission for its proactive regulatory role in advancing the country’s technology revolution through 5G which is going to positively impact all sectors of the economy. No doubt, 5G which will offer better download speed and latency use of more applications (IoT-enabled services), needs robust broadband infrastructure to ride on and the NCC, through the InfraCo initiative is enabling this.
Combating E-waste, IT counterfeiting
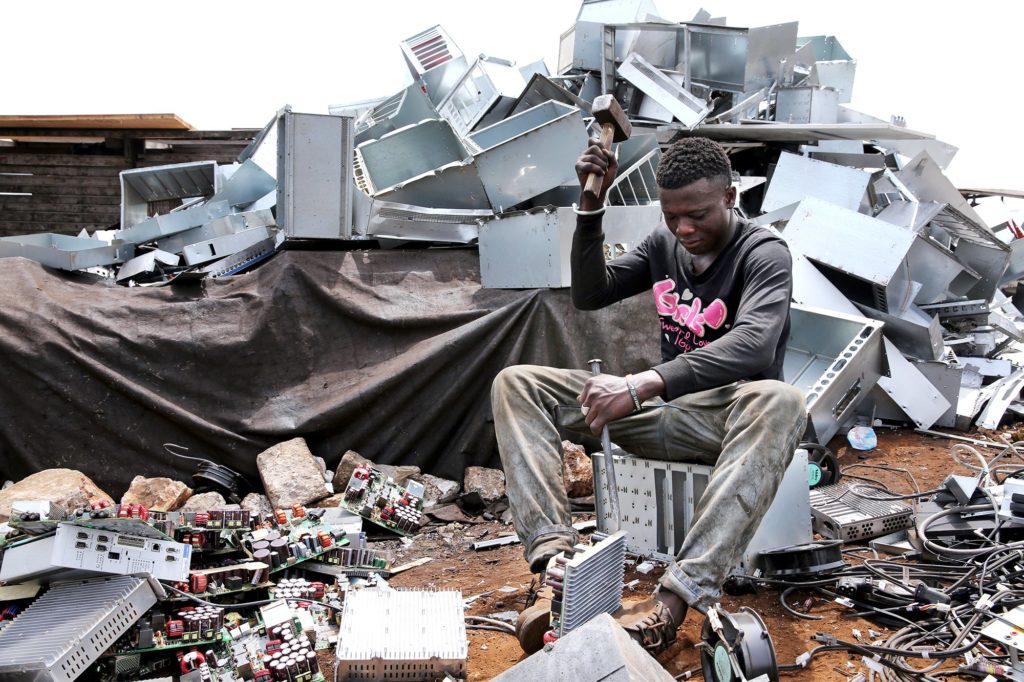

Early in 2019, the Commission unveiled regulation on e-waste and guidelines on distaste recovery at a stakeholder engagement forum held in his office in Abuja. On the e-waste regulations, the Commission sees e-waste as electrical or electronic equipment that is waste, including all components, sub-assembles and consumables that are part of the equipment at the time the equipment becomes waste. Apart from their solid and non-biodegradable nature, some of the toxic elements found in e-waste include lead, mercury, lithium and other ozone-depleting substances. “A recent report by World Economic Forum (WEF) indicates that electronic waste (e-waste) is now the fastest-growing waste stream in the world. It is estimated that this waste stream spiked by about 48.5 million tonnes in 2018. In Africa, the challenge is even direr. In a fast-paced telecoms industry where speed and capacity define the networks, rapid advances in technology make it easier and convenient to change malfunctioning gadgets than to repair them. Also, illegal and predatory e-waste value chain, which encourages the movement of e-waste from developed to the developing countries, adds another layer to the global challenge of handling e-waste,” EVC said at the forum.
The global concern for the regulation of e-waste is two-pronged. The first is the acute awareness of the hazardous properties and the potential risk on human health, as well as their capacity to degrade the environment. The second is the business case and vast potential for wealth creation in recycling e-waste into more benign and productive uses. In Nigeria, due to low Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita/low income and the desperate quest for information, it is estimated that 75 per cent of electronic devices and equipment imported into the country are irreparable and toxic junk. In line with its regulatory mandate and to keep pace with efforts at managing e-waste-related issues, therefore, the Commission developed the draft regulations on e-waste.
According to EVC, the draft regulations represent a holistic intervention aimed at providing clarity and delimiting the responsibilities of various stakeholders in the e-waste value-chain within the telecommunications industry. While the draft is industry-specific, it, nonetheless, keys into other initiatives at national and international levels.
Strengthening Corporate Governance Code with Disaster Recovery Regulation

As a corollary to the regulations on e-waste which was also unveiled during the year under review, it should be stated that the NCC Disaster Recovery Guidelines is actually developed by the Commission to strengthen corporate governance in the telecommunications industry. Basically, a disaster is a serious disruption of the function of a community, society or a business. Disasters often involve widespread human, material or environmental impact, which exceed the ability of the entity to cope with using its immediate resources. The Disaster Recovery Guidelines of the NCC, therefore, ties into the Commission’s wider risk management initiatives introduced by the Code of Corporate Governance launched by the Commission in 2014, which are aimed at protecting telecoms companies from the threat of emergencies in their operations. It covers subjects such as disaster profiling, disaster preparedness, disaster relief and disaster recovery.
Safeguarding national security via SIM registration review
The SIM Registration project supports the agenda to “Facilitate Strategic Collaboration and Partnership” by fostering a synergy/partnership with security agencies towards the adoption and usage of technology innovations to improve security in the country. The Programme is designed to facilitate the registration of all telephone subscribers in the country to mitigate security concerns on the challenges of tracking criminal uses of telephones in the country through Identity and security management and; to ensure the establishment of a credible database of SIM Card subscribers as an enabler to the overall Citizen Identification System.
During the period under review, over 24 million validly registered subscriber records were scrubbed/ cleaned-up (deduplicated) via Automated Fingerprint Identification System (AFIS) in fulfilment of the mandate to establish a credible database of telephone subscribers. The database was also upgraded with additional features such as “Add SIM” and “Update SIM” functionalities as well as the National Identity Number (NIN) field for an improved SIM Registration process and ease of harmonization of SIM registration subscriber data with the National Identity Management Commission (NIMC) when the NIN Regulations come into force. Consequently, in line with the Federal Government directive, the Commission is collaborating with the National Identity Management Commission (NIMC) towards the implementation of the Mandatory Use of National Identification Number Regulations which stipulates the mandatory use of NIN for transactions such as SIM registration, reactivation/retrieval.
Licensing of VAS Aggregator Licences (10 of them)

The dynamism of the industry led to the restructuring of telecoms Value–Added Service (VAS) market for greater growth. Under the watch of the erudite scholar, the Commission has also witnessed a recalibration and repositioning of the sector’s value–added services (VAS) segment, a move that has helped to sanitise the industry. The sub-sector’s current value is estimated at $200 million with potential to grow to over $500 million in the next few years. In line with the restructure, the NCC, in 2019, has awarded the Value Added Services Aggregator licences to ten (10) companies to provide VAS services. It is hopeful that the VAS Aggregator licence will improve innovation, local content, employment opportunities and increase in income stream to both network operators and content developers.
Remarkable decrease in Call Masking activities
Following the enforcement by the Commission for telcos to deploy technology solution across their networks, cases of call-masking or call refiling has reduced drastically. Call masking is when inbound international calls terminate in Nigeria as local number. The Commission quickly noticed that this raises security concerns, competition issue and portends negative economic implications. Then, it swung into action, series of regulatory measures towards curbing the menace of call masking: These include strict compliance monitoring and enforcement by the Commission; imposition of appropriate sanctions by the Commission on licensees involved in call refiling and masking activities; and suspension of numbering plans of some perpetrators and withdrawal of all their inactive numbering plans.
According to Prof Danbatta, other measures taken in this regard include the continuous sensitisation of consumers and other industry stakeholders on the dangers of call masking, which is still ongoing; the development and institution of new reporting requirements on interconnecting licensees that makes it easy and seamless to quickly identify perpetrators of call masking and the Proof of Concept (PoC) commenced in July 2018 with the deployment of technology solutions to monitor, report, apprehend and block SIMs being used for SIM boxing activities and prevent SIM lines from being used for call masking activities. Through the deployment of the technology solutions and continuous monitoring by the Commission for compliance throughout 2019, cases and complaints of call-masking received by the Commission has come to zilch.
Other key projects to deepen digital access in the country

In the year under review, the Commission, embarked on such projects Wireless Internet Cloud, Laptop Project, Computer Based Test (CBT) Centres project and ICT Park project. The Wireless Cloud Project is an initiative to provide a platform for supporting campus-wide wireless access to internet service for teaching, learning, research and development to faculty staff and students of the nation’s Colleges of Education, Polytechnics and Universities and Hospitals through the provision of the necessary infrastructure, including masts, antennas, networking and twelve (12) months bandwidth supply and maintenance support. During the period under review, the Commission successfully implemented the Wireless Internet Cloud in 150 beneficiary institutions at various locations in the country.
The Laptop Project is an initiative to supply, brand, configure and integrate into the cloud laptop computers with e-learning suites in higher institutions across the country. During the period under review, the Commission successfully implemented the supply of laptops in 230 beneficiary institutions at various locations in the country. In line with our strategic Collaboration & Partnerships drive, the Commission is currently implementing the CBT project in Six (6) locations across the Country which includes: FCT, Katsina, Abia, Ondo, Gombe and Anambra States. This is a special intervention Programme by the Commission aimed at establishing state-of-the-art facilities where online examinations can be conducted to entrench efficiency, effectiveness and curb examination malpractices. It is implemented in the 6 Geopolitical Zones in conjunction with the Joint Admission and Matriculation Board (JAMB). The ICT Park, is an initiative to establish a fully functional Digital Industrial Complex (DIC) to drive ICT Development and support Technology Start-Ups in beneficiary States and its environs. The Commission is currently building ICT Parks in Four (4) locations across the Country, namely Kano, Borno, Ogun and Enugu States.
Putting NCC’s Head Office Annex in Mbora, Abuja to use

Among several other internal initiatives embarked upon by the Commission to engender operational efficiency as telecoms regulator in 2019 was the inauguration of a five-storey building constructed by the Nigerian Communication Commission (NCC) essentially meant to complement the Commission’s headquarters building. Located at 1253 Cadastral Zone, Mbora District, Abuja, the project had been abandoned for a long period until Prof Dabatta came on board to see to its completion.
Today, besides providing nearly a hundred-room office accommodation, it was built with facilities such a swimming pool, lawn tennis courts, underground car parks and a 600 -seater auditorium for conferences and seminars. No fewer than five departments of the Commission have since been moved in using the world-class facilities and this has improved their operational efficiency. It has also helped to decongest the Head Office Building of the Commission located at Maitama District, Abuja. More importantly, the continuous use of the 600 -seater auditorium for many of Commission’s activities have resulted in cost-cutting in line with the Federal Government’s directive.